Dear Editors,
Morbihan disease is a persistent inflammatory condition characterized by chronic erythema, non-pitting edema, and swelling, primarily manifesting in the upper two-thirds of the face [1]. While there is mounting evidence suggesting links between Morbihan disease and conditions like rosacea and acne vulgaris, it is noteworthy that this condition can also manifest in individuals without any current or previous medical history. One particular point of contention revolves around the nomenclature of this condition, as Morbihan disease is an eponymous term and is often used interchangeably with solid facial edema. This discrepancy in naming adds to the challenges surrounding the understanding and classifying of this disease. Despite ongoing research and clinical observations, the available information remains limited. Although there are reports of treatment of Morbihan disease with isotretinoin, doxycycline, and minocycline, the treatment is sometimes insufficient and limited. Here, we report a 48-year-old Japanese woman with Morbihan disease that was successfully controlled with dapsone. As far as we searched, there were no other reports administrating dapsone for Morbihan disease other than us.
A 48-year-old Japanese woman presented to our department with complaints of swelling in her right upper eyelid that had persisted for 6 months, despite antihistamine drugs and topical therapy with hydrocortisone butyrate, tacrolimus, and delgocitinib, respectively. On examination, there was moderate edema with erythema confined to the right upper eyelid (Figure 1A). A skin biopsy showed the infiltration of lymphocytes and histiocytes around the perifollicular area in the middle dermis (Figure 1B). There was no neutrophil and giant cell infiltration commonly seen in rosacea. Immunohistochemical examination revealed the proliferation of mast cells and mucin deposition around the hair follicles by Alcian blue staining (Figures 1C, D). Blood tests showed no abnormalities. These findings presented a diagnostic dilemma due to the clinical similarity among Morbihan disease, cutaneous mucinosis, and rosacea as the principal differential diagnoses. However, the absence of the infiltration of neutrophil or giant cells, the localized perifollicular mucin deposition observed in Alcian blue staining and the restriction of lesions to the upper two-thirds of the face led to the conclusive diagnosis of Morbihan disease. Since antihistamines and topical therapy proved insufficient in improving the symptoms, we started doxycycline alone. However, the erythema of the right upper eyelid worsened after doxycycline therapy for 4 months (Figure 1E). Even after the additional administration of prednisolone (PSL) 10 mg daily, the erythema remained unchanged after 1 month. Therefore, we discontinued PSL. Since histopathology showed numerous infiltrations of mast cells, daily 75 mg of dapsone was administered to inhibit the mast cell activities such as the production of reactive oxygen species. Following this, the erythema and swelling of the right eyelid decreased after 4 months (Figure 1F). No adverse effects emerged with oral dapsone. In addition, the patient remained free of recurrence after discontinuing dapsone.
FIGURE 1
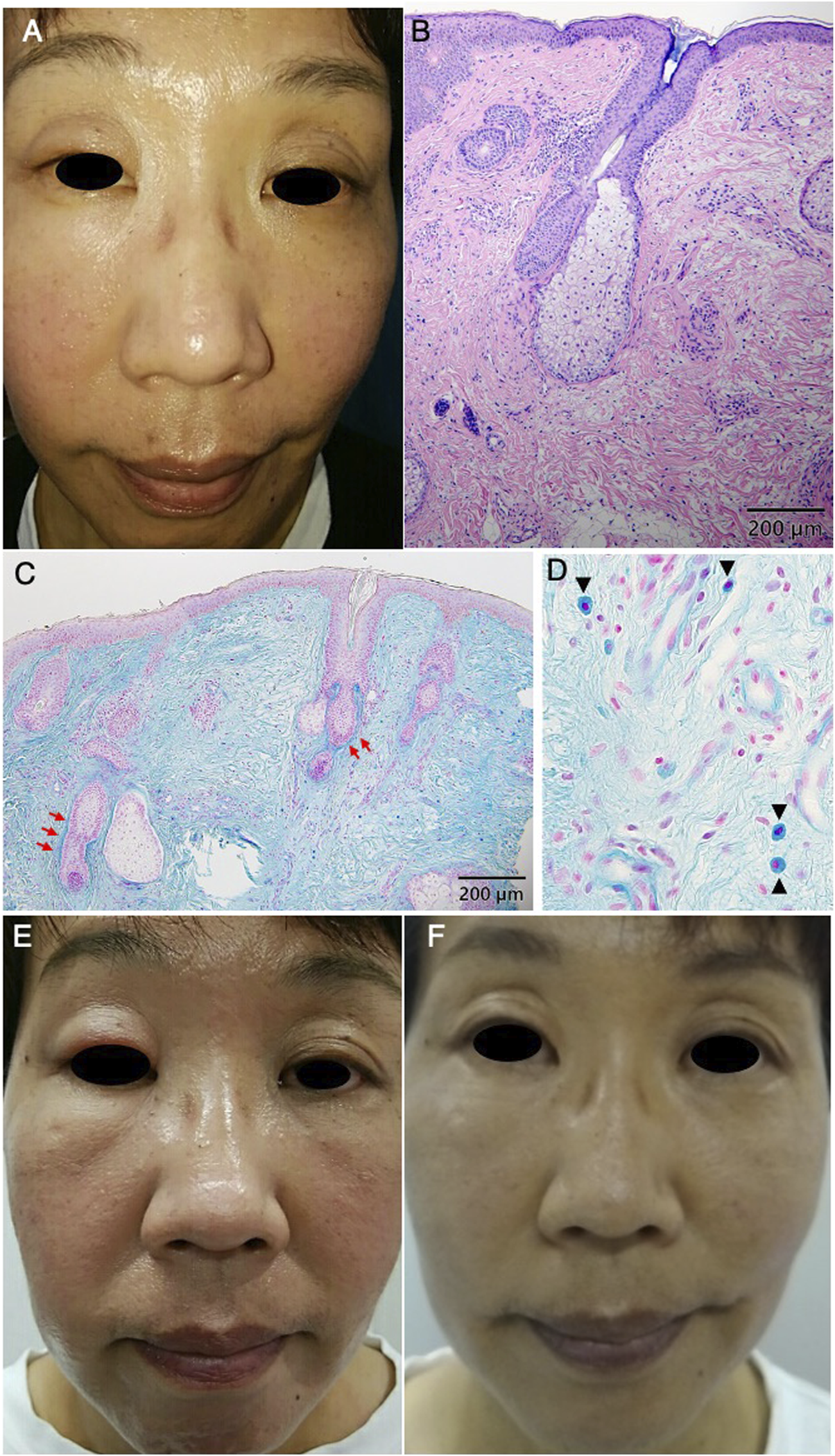
Eyelids were edematous and erythematous at the initial visit (A). Histopathology shows infiltration of lymphocytes and histiocytes around the perifollicular area in the middle dermis (HE) (B). Alcian blue staining shows the mucin deposition around the hair follicles (red arrows) (C). Alcian blue staining reveals the proliferation of mast cells in the dermis (arrowheads) (D). The swelling of the right upper eyelid increased after four month-treatment with doxycycline (E). The swelling and erythema of the eyelids decreased after 4 months of treatment with dapsone (F).
Morbihan disease is a relatively rare disorder initially reported in 1957 by Robert Degos [1]. Seventy-four cases, including our present case, have been reported to date. These cases are comprehensively summarized in Supplementary Table S1, providing a detailed overview of their respective characteristics (Supplementary References S1–S54). There was a male predominance, with a male-to-female ratio of 41:27, although gender information for six cases was unavailable. The median age at the initial presentation was 54.5 years, emphasizing that Morbihan disease predominantly affects middle-aged individuals. Furthermore, the median duration between symptom onset and seeking medical attention was 6 months, underscoring potential delays in diagnosis or patient awareness of the condition. The facial distribution of symptoms was elucidated in 69 cases, with the eyelids including periorbital area being the most commonly affected site in 51 cases (73.9%), followed by the cheeks (11 cases, 15.9%), forehead (4 cases, 5.8%), and nose (3 cases, 4.3%). These findings are consistent with the characteristic localization of Morbihan disease. Treatment modalities such as isotretinoin and tetracycline exhibited efficacy in 20 and 18 cases, respectively, indicating their potential usefulness in managing Morbihan disease. Supplementary Table S2 summarizes the duration of treatment in previous case reports for isotretinoin, the most commonly used treatment for Morbihan disease, and for doxycycline. No reports mentioned using dapsone, a traditionally used agent in dermatology due to its anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties [2]. Dapsone exhibits antimicrobial effects due to its sulfonamide-like capacity to inhibit the synthesis of dihydrofolic acid. Additionally, it possesses anti-inflammatory properties, including the inhibition of reactive oxygen species production, reduction of eosinophil peroxidase’s impact on mast cells, and downregulation of neutrophil-mediated inflammatory responses. These characteristics enable its application in the treatment of a diverse range of inflammatory and infectious skin conditions [3]. The consideration of dapsone introduces a potential new therapeutic avenue; however, caution is warranted due to its association with adverse effects such as dapsone hypersensitivity syndrome, and hematologic complications like blood cell reduction.
Although our case offers a new treatment option for Morbihan disease, certain limitations were encountered. Morbihan disease, being toponymic, may share similarities with conditions like solid facial edema, yet instances not explicitly reported as Morbihan disease might not be captured in our search methodologies. Moreover, Morbihan disease presents a diagnostic challenge due to its diverse differential diseases, with some cases lacking clear differentiation as in the present case. The primary differential diagnoses include rosacea and cutaneous mucinosis. Distinguishing between these conditions is particularly challenging. Morbihan disease is considered to present localized, often pronounced swelling than rosacea. Pathological examination of Morbihan disease may reveal mast cell infiltration, a feature that has also been reported in some cases of rosacea [4]. In addition, it may be useful to observe mucin deposition by alcian blue staining to distinguish cutaneous mucinosis.
Despite advancements, the pathophysiology of Morbihan disease remains elusive. Nevertheless, our findings suggest that dapsone could emerge as a viable therapeutic option, although further research is imperative to validate its efficacy and safety profile in treating this condition. This scarcity of conclusive data underscores its complexity, and further study is needed to better clarify the diagnostic criteria and recommend management strategies for this condition.
Statements
Data availability statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Ethics statement
Because this is a single case report, ethics approval was not required for this study. The studies were conducted in accordance with the local legislation and institutional requirements. The participants provided their written informed consent to participate in this study. Written informed consent was obtained from the participant/patient(s) for the publication of this case report.
Author contributions
YA and KS collected the data, all participated in analyzing the results of the data and reviewing the manuscript, and YM, RF, and HK wrote the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Funding
The authors declare that no financial support was received for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Supplementary material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontierspartnerships.org/articles/10.3389/jcia.2024.12849/full#supplementary-material
References
1.
Degos R Civatte J Beuve-Mery M . Nouveau cas d’oedeme erythemateux facial chronique. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syph (1973) 80:257.
2.
Diaz-Ruiz A Nader-Kawachi J Calderon-Estrella F Mata-Bermudez A Alvarez-Mejia A Rios C . Dapsone, more than an effective neuro and cytoprotective drug. Curr Neuropharmacol (2022) 20(1):194–210. 10.2174/1570159X19666210617143108
3.
Ghaoui N Hanna E Abbas O Kibbi AG Kurban M . Update on the use of dapsone in dermatology. Int J Dermatol (2020) 59:787–95. 10.1111/ijd.14761
4.
Ramirez-Bellver JL Perez-Gonzales YC Chen KR Diaz-Recuero JL Requena L Carlson JA et al Clinicopathological and immunohistochemical study of 14 cases of morbihan disease: an insight into its pathogenesis. Am J Dermatopathol (2019) 41:701–10. 10.1097/DAD.0000000000001378
Summary
Keywords
eyelids, diphenyl sulfone, mast cell, solid facial edema, rosacea
Citation
Morita Y, Koizumi H, Arisawa Y, Fukaura R and Sugawara K (2024) Successful control of Morbihan disease with dapsone: a case report and literature review. J. Cutan. Immunol. Allergy 7:12849. doi: 10.3389/jcia.2024.12849
Received
15 February 2024
Accepted
04 April 2024
Published
16 April 2024
Volume
7 - 2024
Updates
Copyright
© 2024 Morita, Koizumi, Arisawa, Fukaura and Sugawara.
This is an open-access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (CC BY). The use, distribution or reproduction in other forums is permitted, provided the original author(s) and the copyright owner(s) are credited and that the original publication in this journal is cited, in accordance with accepted academic practice. No use, distribution or reproduction is permitted which does not comply with these terms.
*Correspondence: Haruka Koizumi, dermatology.cello@gmail.com
Disclaimer
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.